- drambalkar@yahoo.co.in
- Mon - Sunday 10:00 AM - 02:00 PM
What Is Erythrodermic Psoriasis?
Erythrodermic psoriasis is a severe and rare form of psoriasis, which is a chronic autoimmune skin condition characterized by the rapid buildup of skin cells that results in red, scaly patches or plaques on the skin’s surface. Erythrodermic psoriasis is considered a medical emergency due to its potential to cause serious complications and affect the body’s overall health.
In erythrodermic psoriasis, a significant portion of the skin’s surface becomes inflamed and covered with a red rash that often resembles a severe burn. The condition can be extremely uncomfortable and painful, causing intense itching, burning, and swelling. Additionally, the skin’s barrier function is compromised, which can lead to fluid loss, electrolyte imbalances, and an increased risk of infection.
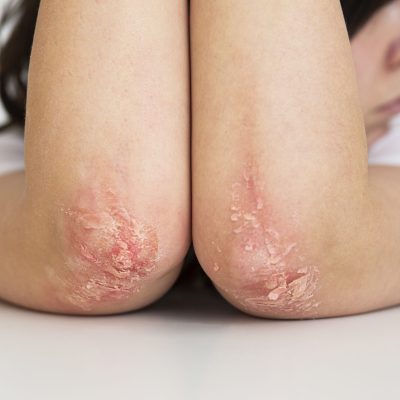
Erythrodermic psoriasis can be triggered by various factors, including:
- Sudden withdrawal from systemic corticosteroids: Abruptly stopping certain medications used to manage psoriasis can lead to a rebound effect and trigger erythrodermic psoriasis.
- Severe sunburn: Extensive sunburn can exacerbate psoriasis and potentially lead to erythrodermic symptoms.
- Infection: Bacterial or viral infections can stimulate an immune response that triggers an episode of erythrodermic psoriasis.
- Certain medications: Some medications, such as lithium, antimalarial drugs, and certain beta-blockers, can induce erythrodermic psoriasis in susceptible individuals.
- Psoriasis flare: Erythrodermic psoriasis can also occur as a severe exacerbation of existing psoriasis, particularly when the disease is not well-controlled.
Erythrodermic psoriasis is a serious condition that requires immediate medical attention. Treatment usually involves hospitalization and may include:
- Topical treatments: In mild cases, topical corticosteroids and moisturizers may be applied to affected areas to reduce inflammation and discomfort.
- Systemic medications: Severe cases often require systemic medications, such as oral corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, or biologic drugs, to control the immune response and reduce inflammation.
- Supportive care: Patients may need supportive measures like fluid and electrolyte balance management, wound care, and infection prevention.
- Avoiding triggers: Identifying and avoiding triggers that can exacerbate the condition is important for preventing future episodes.
- Close monitoring: Regular follow-ups with a healthcare provider are crucial to monitor progress and adjust treatment as needed.
Here are some additional things to keep in mind about erythrodermic psoriasis:
- It is important to stay hydrated and avoid scratching the rash, as this can lead to infection.
- You may need to take time off work or school to rest and recover.
- Erythrodermic psoriasis can be a stressful condition, so it is important to find ways to manage stress.
- There are support groups available for people with erythrodermic psoriasis. These groups can provide emotional support and practical advice.
Conclusion
If you believe you may be dealing with erythrodermic psoriasis or are experiencing severe psoriasis symptoms, it is crucial to promptly seek medical attention from a qualified Ayurvedic skin doctor. They can provide a proper diagnosis and offer appropriate erythrodermic psoriasis treatment. They can also be beneficial for comprehensive care and guidance in managing this condition.

Get in Touch with us Today to Begin Your Journey of Transformation

Contact Us
- Dr.Ambalkars Aayurvedic Research Centre, ARC Bhavan, Vijay Vihar Complex, Evershine City, Last Stop, Vasai (E)
- drambalkar@yahoo.co.in
- +91 9320193201
- +91 9766362776

